Avita are proud of their reputation as industry experts, drawing on generations of experience to craft and create the perfect diamond ring or jewellery for you. It is an important decision you are about to make and we want to help you in every way we can.
The Four C's
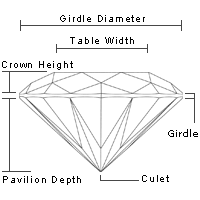
When it comes to understanding the different aspects of a diamond, there are four main characteristics that are commonly used. These are collectively known as the four C's - cut, carat, color, and clarity. If you want to delve deeper into what each of these factors means and how they contribute to the overall value and beauty of a diamond, keep reading below for a comprehensive guide to the four C's.
Diamond Certification
At Avita we will work with the top diamond grading laboratories of the world. All our diamonds over 0.30ct are graded by either GIA, IGI, HRD and other leading diamond grading laboratories from around the world.
If you have a preference on a particular certificate then please Contact Us to let us know and we will happily make your jewellery with your specifications.
Conflict Diamonds
Avita takes steps to ensure its diamonds have not come from conflict zones. We ask and inspect all our suppliers to make sure they do not handle conflict diamonds and that they have subscribed to the Kimberly process thus eliminating conflict diamonds.
Avita Jewellery will never sell or handle diamonds without having guarantees the diamond is conflict free.
Learn More
Men's Guide To Buying The Perfect Engagement Ring
Buying an engagement ring can be a daunting task, especially if you don't know much about jewellery. Here are some tips to help you choose the perfect engagement ring for your signif...
Why Chose A Lab Grown Diamond Engagement Ring?
We often get asked why should I choose a Lab created diamond over a Moissanite or a natural diamond? It depends on your preferences at the end of the day however, La...
Learn All About Different Diamond Shapes
Whether you're shopping for an engagement ring or simply interested in learning more about diamonds, we will guide you through the different diamond shapes and their features...